20.04.2017
 OntoMedRisk
OntoMedRisk
Medizinisches Personal arbeitet oft unter großer physischer und psychischer Belastung, wodurch sich die Wahrscheinlichkeit von Fehlern und unerwünschten Ereignissen erhöht. Im Rahmen des OntoMedRisk-Projekts wird daher eine agentenbasierte, ontologie-gestützte Softwarelösung entwickelt, um das Auftreten solcher Ereignisse zu minimieren. Das Ziel ist es, Ärzten und medizinischem Fachpersonal eine technische Unterstützung zur prozessübergreifenden Risikoerkennung und Fehlervermeidung zur Verfügung zu stellen. Die Softwarelösung soll dynamisch eine Risikoanalyse auf der Grundlage von verfügbaren Datenquellen (wie der Patientenakte, dem KIS oder Checklisten, aber auch basierend auf realen Situationen im Prozess) durchführen. Daraufhin sollen kontextsensitive Hinweise zur Fehlervermeidung für die am Prozess beteiligten Fachkräfte generiert werden.
02.12.2020
 OncoControl
OncoControl
Project description
The multidisciplinary treatment of patients in head-and-neck tumor therapy is a challenging problem for the clinicians involved due to the huge amount of available information. This information stems from diagnostic methods such as patient history, blood count and biopsy results as well as medical imaging techniques like computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). In order to support the clinicians, these complex information entities must be processed in a meaningful way. The project OncoControl is the realization of a web-based system which is intended to support the head and neck oncology in exploration, analysis and management of patient data.
Research goals
The central idea in developing OncoControl is the improvement of the oncological therapy decision-making processes in the field of complex head and neck tumors, improving existing work and treatment processes as well as a support of the decision-making process in the tumor board through the use of endoscopy images and 3D tumor reconstructions alongside the current unused slice images from computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Additionally, a new and innovative form of presentation, the “treatment summary”, supports the clinicians after opening the patient file with a compressed representation of all relevant information in the current treatment step and provides a quick overview of the current patient status.
Project priorities
- Automatic centralized information aggregation
- Improving data quality and prioritization of information
- Automatic generation of “treatment summary” and clinical documents
- Computerized TNM classification
- Verification, integration and evaluation of the overall system in clinical use
Previous research results
Associated publications:
Birnbaum, Zebralla, Boehm, Dietz, Neumuth. „Metric Learning for TNM-Classifications of Patients with Head and Neck Tumors“. CARS 2016 Proceedings. Heidelberg, 2016.
Meier, Jens, Stefan Bohn, Bernhard Glaser, Klemens Birnbaum, Andreas Boehm, und Thomas Neumuth. „The Treatment Planning Unit: Concept and realization of an integrated multimedia decision support system for multidisciplinary team meetings“. In MedInfo 2015. Sao Paolo, 2015.
Meier, Jens, Andreas Dietz, Andreas Boehm, and Thomas Neumuth. “Predicting Treatment Process Steps from Events.” Journal of Biomedical Informatics 53 (February 2015): 308–19. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2014.12.003.
Outlook
The development of the clinical information system OncoControl allows the physician to get all information about existing patients in a consistent and structured way as well as to retrieve clinical documents such as medical reports or surgery reports. Furthermore, OncoControl allows the clinicians to create and make use of existing information for clinical trials, quality management or conducting clinical certifications. Building on the established central database innovative and knowledge-based methods will assist the clinicians, for example for the TNM classification or document generation in diagnosis, treatment strategy, documentation, as well as presentation and patient education and thus facilitate their clinical practice and the communication between professionals. The use of automated procedures should also pave the way for standardized procedures and comparable analysis results.
21.09.2020
 EVENTOR
EVENTOR
Project description
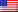
Eventor is a project in cooperation with the SWAN – Scientific Workflow Analysis GmbH. The aim of the project is the development of concepts for interconnecting process logic and integration technologies for intra- and peri-operative purposes. This allows the semi automation of data exchange and interaction between medical devices based on the surgical situation. Hence, novel forms of surgical assistance might be developed. Additionally, human machine interaction might be simplified to unburden the surgeon and the OR-staff. The implementation is mostly based upon existing integration technologies as well as a tailored rule set for handling of process information. The developed concepts and prototypical implementations will be evaluated for selected clinical fields of application.
Research goals
The increasing number of medical devices and information systems around the operating theatre lead to additional administrative workload. The project evaluates the application of process information to simplify these tasks. This includes the following research goals:
- integration of existing medical devices and information systems with a process logic,
- modeling of surgical requirements, based on surgical process model concepts,
- development of a tailored rule set for process information,
- implementation and evaluation of prototypical systems for selected clinical use cases.
Priorities of the project
Eventor focusses on three research topics:
- complex modeling of surgical procedure,
- situation-aware communication and interaction of medical devices,
- dynamic information exchange based on surgical workflow.
Previous research results
Currently, we analyzed clinical fields of application and their requirements towards dynamic integration of process logic. Furthermore, existing technologies in various fields of research had been evaluated.
Outlook
Eventor develops and evaluates concepts for dynamic interconnection of process logic and integration technologies for various clinical applications. The developed concepts and prototypes will contribute to the development of situation-aware medical devices.
03.09.2020
 OR.NET
OR.NET
Project description
OR.NET is a collaborative project funded by the BMBF program “ICT 2020 – Research for Innovation”. The goal of the initiative is to develop basic concepts for safe dynamic networking of medical devices within the operating room. Especially the automatic dynamic networking of computerized medical devices and the interaction of these devices with medically approved software is of particular interest in the medical technology domain. The close cooperation between manufacturers, clinical operators, academia and regulatory bodies facilitates new ways of designing software architectures for the future hospital. The focus is on IT in the operating room and the pre- and postoperative phases, which also connects systems for surgical planning, OR management, as well as diagnosis and treatment. A special focus is on networking, interoperability and the safe operation of the OR infrastructure. To conceptualize and define new standards, research is being conducted regarding risk analysis, safety, security, interoperability and IT infrastructure together with standards committees (VDE, DIN, DKE, IHE …).
Research goals
The overall goal of the OR.NET project is the integration of medical devices in the operating room based on standardized communication technologies. The overall goal is divided into the following sub-projects:
- Networking of medical devices based on a SOA with the use of existing internet “standards” such as WSDL, SOAP, and XML Schema,
- Transition of the developed OR.NET solutions into international standards,
- Development of appropriate operating,
- Design, evaluation and implementation of software components for the digital operating room,
- Technologies developed during the project will be implemented in clinical demonstrators.
ICCAS sub-projects
The overall project OR.NET is conducted by 46 project partners. The developments at the ICCAS comprise the following topics:
- Clinical and technological requirements analysis,
- Integration of results from preliminary projects (e.g. smartOR) and support of clinical and industrial partners,
- Definition of an IT-architecture for the integrated operating room,
- Design, evaluation and implementation of software components for the digital operating room,
- Development and implementation of communication interfaces for information systems, medical devices and communication gateways,
- Participation in the definition of new standards for medical device interoperability,
- Implementation of a demonstrator operating room in Leipzig,
- Evaluation and validation of the overall concepts within the clinical environment.
Previous research results
Several requirement analyses have been carried out in collaboration with clinical partners. Multiple surgical interventions from neurosurgery and ENT have been identified as reference workflows for OR.NET. From these interventions technical requirements, regarding device integration and medical device interoperability, are being derived. Together with technical project partners several workshops have been conducted to define communication requirements for medical device integration using plug-and-play technologies. As a result, this leads to formal device abstractions that are being used to define an integration-architecture with appropriate interface technologies.
Cooperation partners
A total of 57 partners from research and industry under the leadership of the University Hospital Heidelberg, Munich Technical University and RWTH Aachen University are involved in this cooperation project.
Carl Zeiss Meditec, AGConworx Technology GmbH, DIN – Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V., Forschungsstelle für Medizinproduktrecht (FMPR), Fraunhofer FIRST, Fraunhofer MEVIS, how to organize, IHE Deutschland e. V., Ingenieurbüro Wolfgang Blocher, Inomed Medizintechnik GmbH, KARL STORZ, Klinikum Rostock, Klinik für Anästhesiologie und Intensivmedizin KLS Martin Group, LOCALITE GmbH, MedPlan Engineering GmbH, MT2IT, qcmed GmbH Quality Consulting Medical, Rhön-Kliniken AG, Richard Wolf GmbH, RWTH Aachen, Lehrstuhl für Medizinische Informationstechnik (MedIT), RWTH Aachen, Lehrstuhl für Medizintechnik (mediTEC), Siemens HealthCare, STARC medical GmbH, SurgiTAIX AG, Synagon GmbH, Söring GmbH, TRILUX GmbH & Co. KG Medical Technology, TU München, Institut für Informatik, Robotics and Embedded Systems, TU München, Lehrstuhl für Automatisierung und Informationssysteme, TU München, Lehrstuhl MIMED im Bereich Mechatronik, TU München, Minimal-invasive Interdisziplinäre Therapeutische Intervention (MITI), Uniklinik der RWTH Aachen, Integrierte Teleanästhesiologie, Uniklinik der RWTH Aachen, Klinik für Anästhesiologie, Uniklinik der RWTH Aachen, Orthopädische Klinik, Uniklinik Leipzig, Klinik für HNO, Uniklinik Leipzig, Klinik für Neurochirurgie, Uniklinik Tübingen, Radiologische Universitätsklinik, Uniklinik Tübingen, Universitäts- Frauenklinik, Uniklinik Tübingen, Universitätsklinik für Radiologie, Uniklinik Tübingen, Universitätsklinik für Urologie, UniTransferKlinik GmbH, Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg, Zentrum für Informations- und Medizintechnik, Universitätsklinikum Schleswig- Holstein, Chirurgie, Universitätsklinikum Schleswig- Holstein, Stabsstelle IT, Universität Rostock – Institut für Angewandte Mikroelektronik und Datentechnik, Universität zu Lübeck, Institut für Softwaretechnik und Programmiersprachen, Universität zu Lübeck, Institut für Telematik, Universität zu Lübeck, Institut für Medizinische Informatik, VDE Verband der Elektrotechnik Elektronik Informationstechnik, VISUS Technology Transfer GmbH, Vital Images Germany GmbH, Ziehm Imaging GmbH, MEDNOVO Medical Software Solutions GmbH
17.11.2020
 Surgery Planning Software for Vascular Prostheses Implantation
Surgery Planning Software for Vascular Prostheses Implantation
Project description
The project deals with the definition of requirements for surgical planning software, which will focus on the surgical use of stent grafts. Furthermore the feasibility of a physically based simulation model for the assessment of stent graft fixation and sealing potential are studied and requirements for a software module for analyzing the results in the medical environment will get defined. The writability of the resulting data is based primarily on existing standards. Required extensions are also included.
Main topics of the project
- Implant selection in endovascular surgery
- Integration of Finite Element Method (FEM) in a medical planning software
- Human-Machine Interaction
- Workflow analysis
- Medical standards: DICOM
Problem
A common complication of endovascular aortic aneurysm exclusion is the slipping of the stent graft resulting in insufficient sealing of the vessel. This post-operative complication may be associated with the selection of the vascular implant in the compound. In particular the determination of the stent graft oversize for the fixation of the implant in the vessel is of crucial importance.
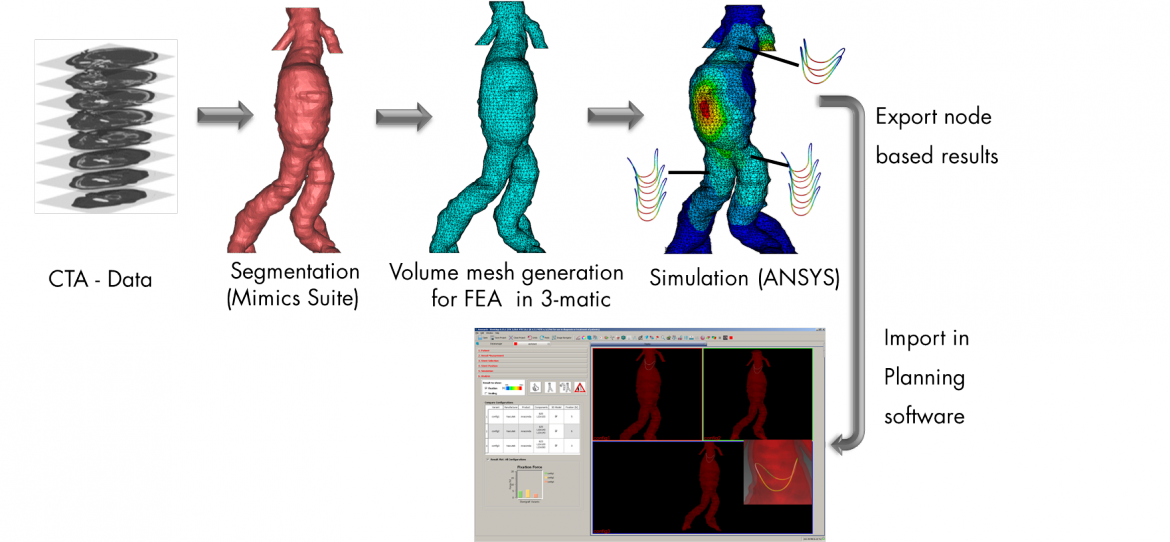
Figure 1: Integration of Calculation Results (FEM Model) into Medical Planning Software for the Evaluation of Stent Graft Properties (Fixation and Sealing Potential)
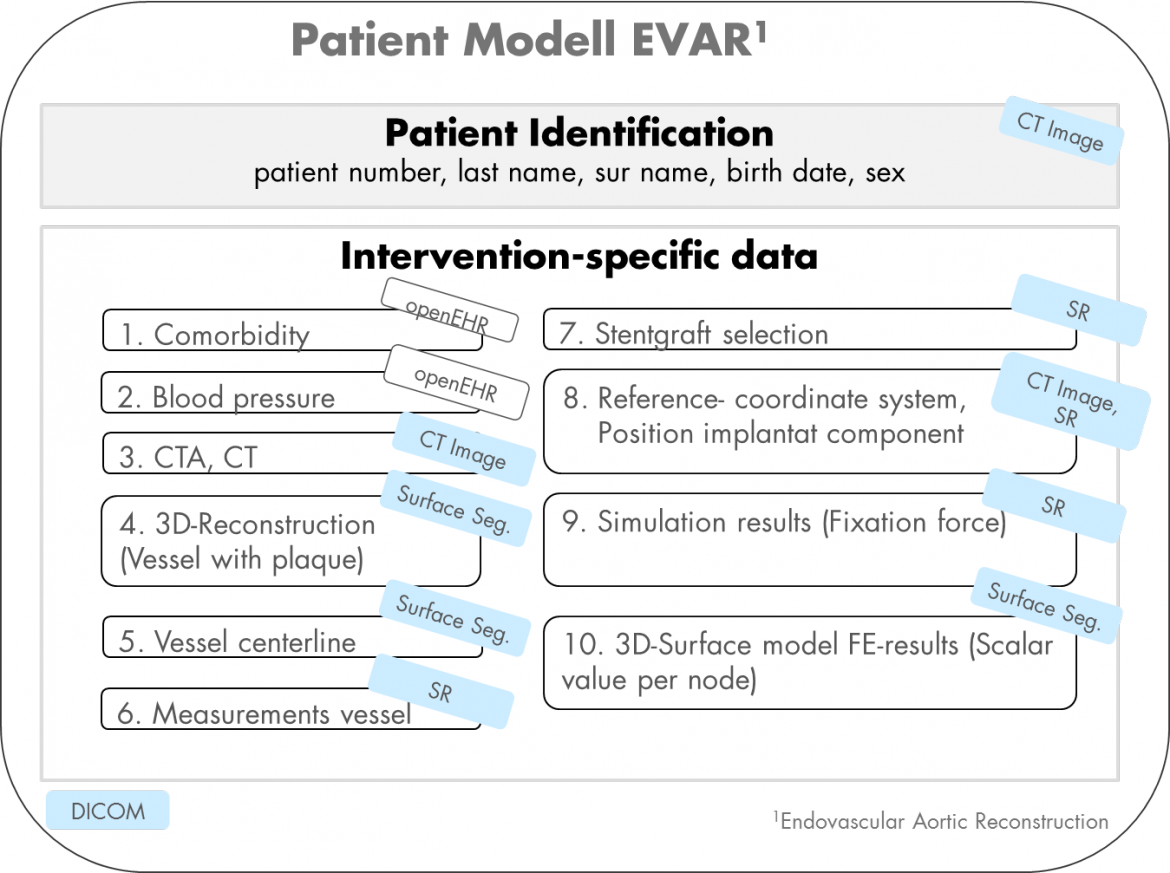
Figure 2: EVAR Patient Model: Description of all Intervention Relevant Data. Integration of Simulation-Specific Data Using Standardized Data Structures
Research goals
- Integration of FEM results in a medical scheduling software for better assessment of migration and leakage risk in endovascular aortic aneurysm exclusion
- Support the physician in selecting a suitable vessel implant through the quantified assessment of stent graft properties in the implanted state